Message From The Chairman
Creative Innovation Blooming New Manufacturing Economy
As machine tools are rightly called mother machines, machine tool producers have a significant role to play in helping the global economy escape the current tunnel of hardship, providing the leverage to enhance productivity in every manufacturing sector.
‘12 Korean & Global Machine Tool Industry
Korea Joins Big-Four League in Production
In 2012, Korea passed Italy to become the world’s fourth largest machine tool producing nation, trailing only China, Japan and Germany.
2012 Scoreboard
Registering Record High Exports & Trade Surplus
Despite the overall recession at home and abroad, Korea registered record highs in machine tool exports and trade balance, reflecting the success of the nation’s global outreach initiatives.
- Production Increases Thin 1.0% to 6.4 Trillion Won
- Order Receipts Fall Sharply
- Imports Tumble 16.87%, Registering US$1.49 Billion
- Exports Surge 10.4% to US$2.55 Billion
2013 Outlook
Gradual, Mild Recovery Looms
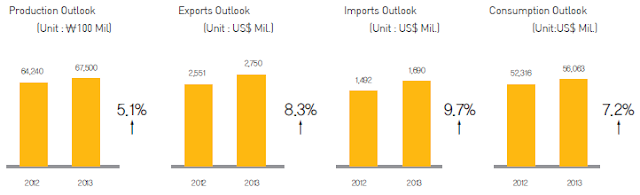
- Production Projected for 5.1% Rise to 6.75 Trillion Won
- Near Double-Digit Increase Forecast for Imports at US$1.69 Billion
- Exports Expected to Top US$27 Billion with 8.3% Expansion
- Consumption Predicted to Rise 5.8% to 5.6 Trillion Won
End-User Industries
Beyond Constraints, Recovery Picking Up Steam Across the Board
- Automobile Exports Expected to Bounce Back with 3.3% Rise
- Shipbuilding Creating New Blue-Ocean with Offshore Platforms
- Machinery Production Scaled at 454 Trillion Won in 2013
- Steel Sees Demand Increase at Home & Abroad
- 2013 Petrochemical Investment Projected at 6.3 Trillion Won
- IT Remains Growth Engine for Creative Korea
- Convergence Creating New Opportunities in Next-Gen Growth Engines
- Highlights of Korean Industrial Policies in 2013
About KOMMA
Success Partner for Machine Tool Industry at Home & Abroad
Since it was established in 1979, the Korea Machine Tool Manufacturers' Association(KOMMA) has played a pivotal role in the dynamic development of the Korean machine tool industry.
KOMMA Members
Your Prospective Business Partners
Introducing the more than 182 member companies of KOMMA with a focus on products and contact points to increase your leverage in Korea and at the hub of Asia.
Statistics and More
Introducing 17 statistical references and valuable information to fuel your advance into Korea’s manufacturing markets.
SIMTOS 2014
Generator of New Opportunities & SMILE
With the goal of being a business angel for exhibitors, buyers and visitors, SIMTOS 2014 organizers are determined to faithfully fulfill the mission of being Your Sales Dept. 2.